Streptavidin Conjugates
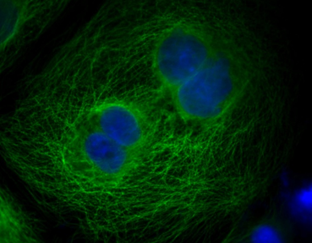
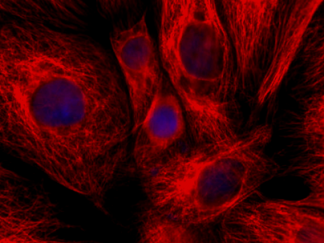
Streptavidin-based amplification techniques are widely used in flow cytometry, fluorescent imaging, western blotting, and microplate-based detection for increased signal output and greater sensitivity. Streptavidin conjugates can be applied to specific detection of a variety of proteins, protein motifs, nucleic acids and other molecules. Streptavidin has an extremely high binding affinity for biotin, which can be exploited to offer a powerful secondary method of detection when the streptavidin is conjugated to a fluorescent protein, enzyme or gold nanoparticle.
Streptavidin conjugates are often utilized to detect biotinylated molecules in common research applications such as:
- Immunofluorescence microscopy
- In Situ Apoptosis (TUNEL) assay, visualized with fluorescence
- In Situ hybridization
- Flow cytometry
- Tetramer staining
- ELISA
- Microarrays
- Western blot
Streptavidin can bind to four moles of biotin per mole of protein, and its high affinity reaches approximately 10,000-15,000 Da. Streptavidin lacks the carbohydrate side chains present on avidin and has an isoelectric point of 6.5 to avidin’s 10, far closer to that at which most useful biological interactions occur.
Streptavidin can be used for the coating of solid phases to immobilize or purify biotin-labeled or 2-iminobiotin-labeled molecules. Its conjugation with enzyme or fluorescein is widely used in immunological detection assays, such as the streptavidin/biotin system.
Showing all 3 results