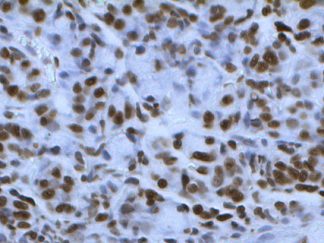
In Situ Detection of Apoptosis
Apoptosis is a highly regulated process of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. It involves a series of biochemical events that lead to characteristic morphological changes and ultimately cell death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, chromosomal DNA fragmentation, and global mRNA decay. Apoptosis plays a critical role in various processes including normal cell turnover, proper development and functioning of the immune system, hormone-dependent atrophy, embryonic development, and chemical-induced cell death.
There are various methods available for the detection of apoptotic cells in situ, including the commonly used Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) and caspase 3 immunohistochemistry (IHC). These methods enable researchers to study and understand the mechanisms underlying apoptosis, and their applications range from basic research to clinical diagnostics.
Showing all 5 results
-
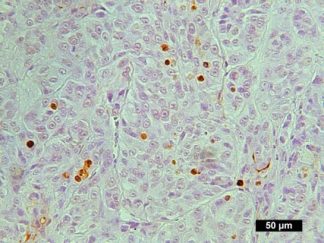
In Situ TUNEL Apoptosis Detection Kit (50 Assays)
SKU: VB-4005 $290.00 -
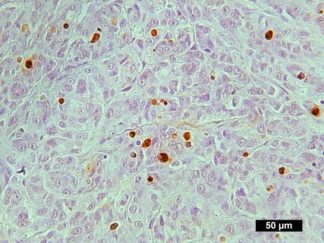
In Situ TUNEL DAB Apoptosis Detection Kit (50 Assays)
SKU: VB-4005D $380.00 -
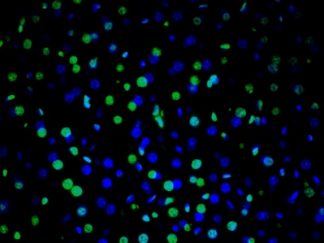
In Situ TUNEL Andy488 Apoptosis Detection Kit (50 Assays)
SKU: VB-4005G $350.00 -
In Situ TUNEL Andy594 Apoptosis Detection Kit (50 Assays)
SKU: VB-4005R $350.00
Showing all 5 results