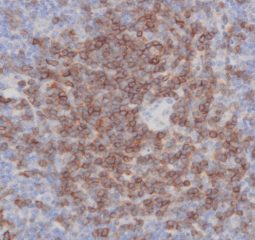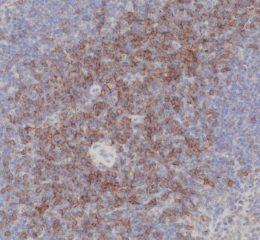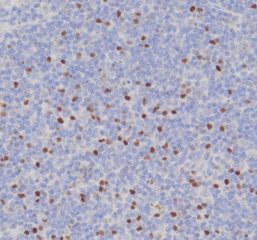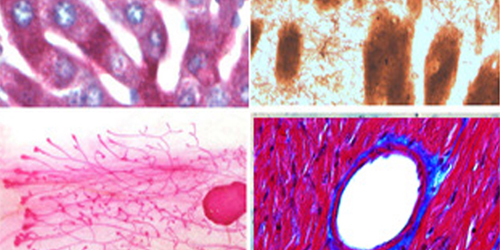
Tissue Microarray (TMA) Services
Our comprehensive Tissue Microarray (TMA) services support both FFPE and frozen sample formats, enabling high-throughput tissue analysis for research and diagnostic applications. We provide precision construction, sectioning, staining, and expert pathology evaluation—delivering high-quality results tailored to advanced spatial biology platforms such as CosMx™ and Xenium™ and routine hight-troughput tissue analysis.
FFPE Sample TMA Services
- FFPE Sample TMA Construction
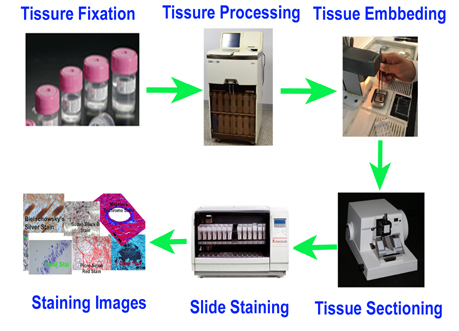
We construct custom TMAs from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue blocks with high precision, ensuring consistent core placement and layout. - FFPE Sample TMA Sectioning
Our expert histotechnologists section FFPE TMAs with accuracy to preserve tissue morphology and antigenicity for downstream applications. - Restricted Area TMA Sectioning (CosMx/Xenium Compatible)
We offer precise TMA sectioning targeting restricted regions of interest—fully compatible with high-resolution spatial platforms such as CosMx or Xenium. - FFPE TMA H&E Staining
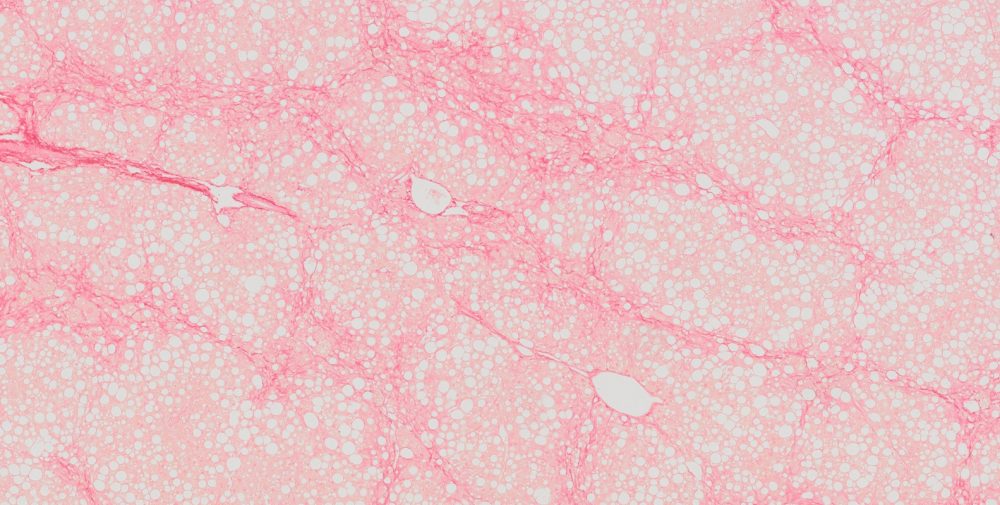
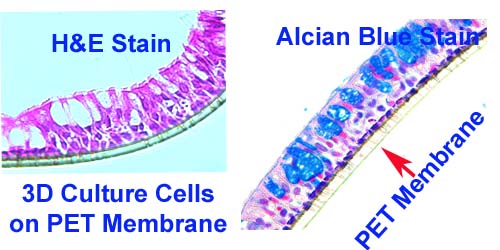
High-quality hematoxylin and eosin staining is performed on FFPE TMA slides for clear visualization of tissue architecture. - Pathology Description by Certified Pathologist
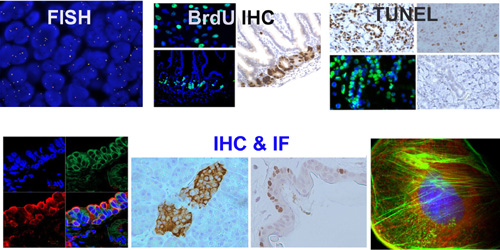
Each TMA slide can be reviewed and described by a board-certified pathologist, providing detailed annotation and quality assessment.
Frozen Sample TMA Services
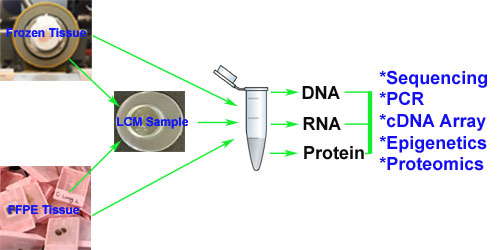
- Frozen Sample TMA Construction
We construct TMAs from fresh-frozen tissue blocks, maintaining tissue integrity and biomolecule preservation for specialized applications. - Frozen TMA Sectioning
Our cryosectioning services deliver high-quality, uniform sections from frozen TMAs, ready for downstream analysis. - Frozen TMA H&E Staining
We offer optimized H&E staining for frozen TMA sections, providing excellent contrast and tissue detail for histological evaluation.